Warehouse / Facilities Trends for 2025: Automation and Sustainability Take Centre Stage
As we approach 2025, the warehouse and facilities landscape is transforming remarkably. Technological advancements and shifting consumer demands are reshaping how these spaces operate.
Automation, data-driven decision-making, and sustainable practices will define the future of warehousing.
Warehouse automation is set to revolutionise operations, with advanced robotics and autonomous vehicles reducing manual labour and increasing efficiency.
This shift towards automated systems will streamline processes and address the labour shortages that have plagued the industry.
Sustainability is becoming a top priority for warehouses and facilities. Companies are increasingly adopting eco-friendly practices, from energy-efficient lighting to green building materials.
These changes reduce environmental impact and lead to significant cost savings in the long run.
The Evolution of Warehousing in the Digital Age
Digital technologies are revolutionising warehouse operations, enhancing efficiency and productivity.
Advanced systems and data-driven approaches transform traditional facilities into smart, interconnected hubs.
The Impact of Digital Transformation
Digital transformation is reshaping warehouses, driving unprecedented efficiency and accuracy. Warehouse digitisation is crucial for meeting growing demand and addressing industry pressures.
Automated systems and robotics streamline operations, reducing manual labour and errors.
Internet of Things (IoT) devices enable real-time tracking of inventory and assets. This connectivity enhances visibility and control across the supply chain.
Smart sensors monitor environmental conditions, ensuring optimal storage for sensitive goods.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms optimise warehouse layouts and picking routes. These technologies adapt to changing demand patterns, improving space utilisation and worker productivity.
Digital Twins in Warehouse Management
Digital twins create virtual replicas of physical warehouses, offering powerful simulation capabilities.
These models allow managers to test process changes and optimisations in a risk-free environment.
Real-time data integration enables digital twins to reflect current warehouse conditions accurately. This synchronisation supports proactive decision-making and rapid problem-solving.
Facility planners use digital twins to design more efficient layouts and workflows. The technology helps identify bottlenecks and optimise resource allocation before implementing changes in the physical space.
Data-Driven Decision Making and Predictive Analytics
Data optimisation is becoming central to modern warehouse management.
Advanced analytics tools process vast amounts of operational data, uncovering insights to drive performance improvements.
Predictive analytics forecast demand patterns and potential disruptions. This foresight enables proactive inventory management and resource planning, reducing stockouts and overstock situations.
Machine learning algorithms analyse historical data to optimise picking strategies and route planning. These data-driven approaches significantly enhance order fulfilment speed and accuracy.
Real-time dashboards provide managers with key performance indicators at a glance. This visibility supports agile decision-making and rapid response to changing conditions.
Sustainable Practices in Warehouse Operations
Sustainable warehousing is becoming increasingly crucial in modern logistics. Companies are adopting eco-friendly strategies to reduce environmental impact whilst improving efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Sustainable Warehousing Trends
Sustainable practices in warehousing are reshaping the industry.
Energy-efficient lighting systems with motion sensors are commonplace, significantly reducing electricity consumption.
Many facilities implement green building designs, incorporating natural light and proper insulation to minimise heating and cooling needs.
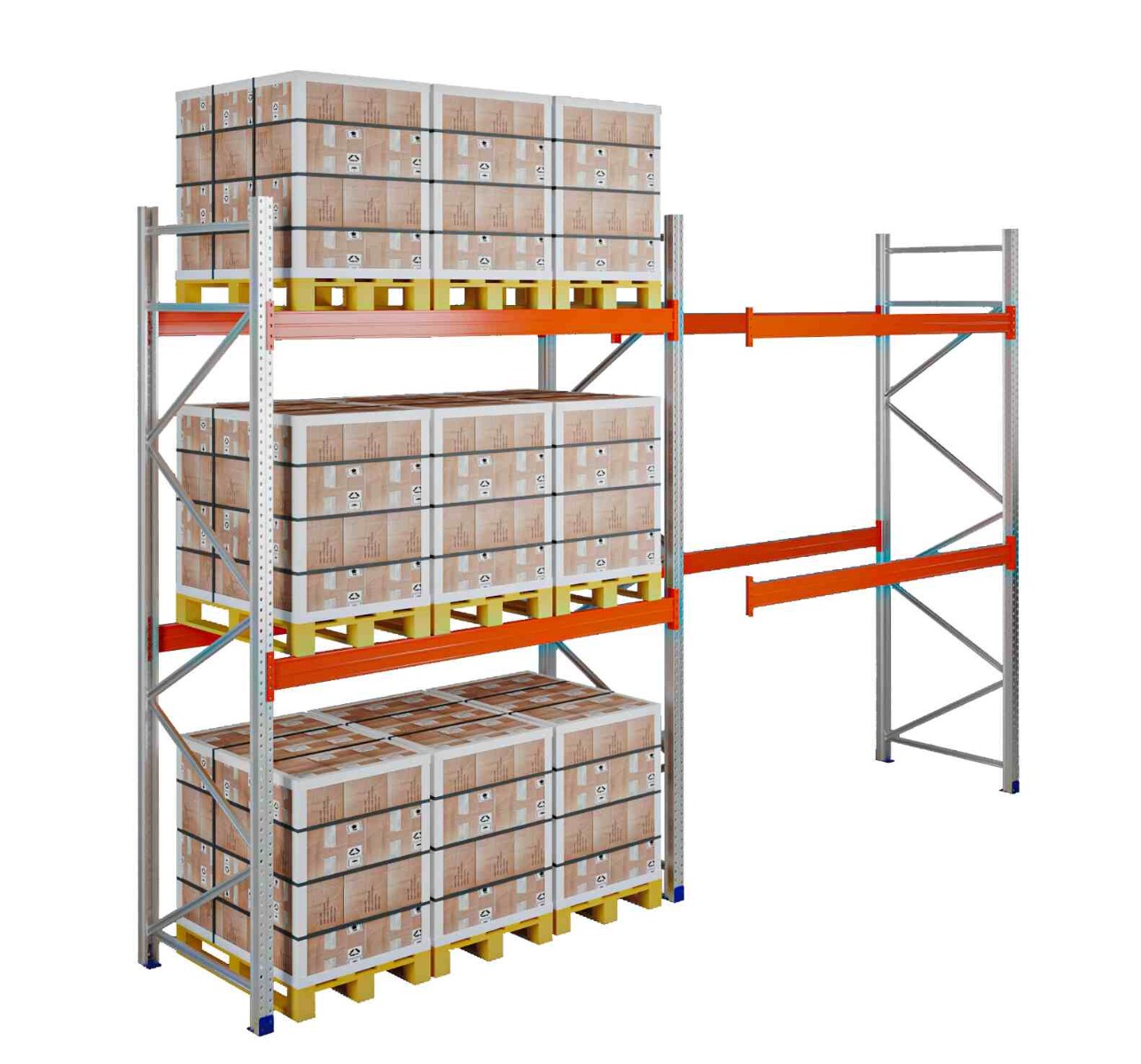
Warehouse automation is pivotal in sustainability efforts. Automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) optimise space utilisation, reducing warehouses’ overall footprint.
These systems also enhance inventory accuracy, reducing waste from overstocking or obsolescence.
Water conservation measures are gaining traction. Rainwater harvesting systems and low-flow fixtures are being installed to reduce water usage.
Some warehouses are even implementing greywater recycling systems for non-potable uses.
Energy Consumption and Carbon Emissions Reduction
Warehouses are major energy consumers, but innovative solutions are helping to curb this issue. Solar panels and wind turbines are increasingly installed on warehouse roofs and surrounding areas, generating clean energy on-site.
Electric forklifts and other material handling equipment are replacing their fossil fuel-powered counterparts, significantly reducing carbon emissions.
Many facilities also implement smart energy management systems that optimise power usage based on real-time demand.
Improved insulation techniques and the use of thermally efficient materials in construction are helping to reduce heating and cooling needs.
Some warehouses even explore geothermal heating and cooling systems for further energy savings.
Green Initiatives in Global Supply Chains
Sustainability in warehousing extends beyond individual facilities to encompass entire supply chains.
Companies increasingly adopt recyclable and biodegradable packaging materials to reduce waste and environmental impact.
Reverse logistics processes are refined to handle returns more efficiently, reducing transportation emissions and waste.
Many warehouses implement advanced waste sorting and recycling programmes to minimise landfill contributions.
Collaborative efforts between suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors are leading to more efficient transportation routes and load consolidation, reducing overall carbon emissions.
Some companies are even exploring using electric or hydrogen-powered lorries for short-haul deliveries.
Innovations in Automation and Robotics
Warehouses are undergoing a technological revolution, embracing cutting-edge automated systems and robotic solutions. These advancements are reshaping operations, enhancing efficiency, and addressing labour challenges in the logistics sector.
The Rise of Autonomous Mobile Robots
Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) are transforming warehouse operations.
These versatile machines navigate independently, optimising routes and adapting to changing environments. AMRs excel in order picking, inventory transport, and sortation tasks.
Key benefits of AMRs include:
- Increased productivity
- Reduced labour costs
- Enhanced safety
- Scalable operations
AMRs utilise advanced sensors and AI algorithms to avoid obstacles and collaborate seamlessly with human workers.
This technology enables warehouses to handle fluctuating demand more effectively, especially during peak periods.
Recent innovations in AMR design focus on improved battery life, faster charging, and enhanced payload capacity.
These improvements allow for longer operational hours and the handling of heavier items, further expanding their utility in diverse warehouse settings.
Advancements in Drone Technology for Inventory Management
Drones are revolutionising inventory management in large-scale warehouses. These aerial devices offer rapid and accurate stock counts, especially in hard-to-reach areas.
Drone technology is precious for high-bay storage facilities and expansive distribution centres.
Key applications of warehouse drones include:
- Cycle counting
- Asset tracking
- Damage inspection
- Security surveillance
Advanced imaging systems and AI-powered analytics enable drones to capture detailed inventory data quickly.
This technology significantly reduces the time and labour required for manual stock checks, improving inventory accuracy and reducing operational costs.
Emerging drone innovations focus on extended flight times, improved obstacle avoidance, and enhanced data processing capabilities.
These advancements are making drone-based inventory management more efficient and reliable.
Cobot Integration in Modern Warehousing
Collaborative robots, or cobots, are designed to work alongside human employees, combining the strengths of both.
These versatile machines enhance productivity in various warehouse tasks without compromising worker safety.
Cobot applications in warehousing include:
- Order picking assistance
- Packing and unpacking
- Quality control inspections
- Repetitive task automation
Cobots feature advanced sensors and safety systems, allowing them to operate in close proximity to humans without protective barriers.
This flexibility enables warehouses to automate processes while maintaining a human workforce for complex decision-making tasks.
Recent innovations in cobot technology focus on improved dexterity, enhanced learning capabilities, and easier programming interfaces.
These advancements are making cobots more adaptable to diverse warehouse environments and tasks.
Technological Advancements and Their Impact on Logistics and Supply Chain
Emerging technologies are reshaping logistics and supply chain operations, driving efficiency and innovation. These advancements transform how goods are tracked, managed, and delivered across global networks.
Integration of the Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things enhances visibility at every supply chain step.
IoT devices provide real-time inventory level data, shipment location, and equipment status.
Smart sensors monitor temperature-sensitive goods, ensuring product quality during transport. Connected vehicles offer precise tracking and optimised route planning.
IoT-enabled warehouses utilise automated guided vehicles and smart shelving systems.
These innovations streamline operations, reduce errors, and improve inventory accuracy.
Improving Logistics with AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are revolutionising logistics decision-making. AI-powered forecasting equips businesses with intelligence to prevent disruptions and optimise inventory levels.
Machine learning algorithms analyse vast datasets to predict demand patterns and identify potential bottlenecks.
This enables proactive problem-solving and more efficient resource allocation.
AI chatbots and virtual assistants enhance customer service by providing real-time shipment updates and handling routine inquiries.
These tools free up human staff to focus on more complex tasks.
Enhancing Supply Chain Efficiency with Automation
Automation technologies are transforming warehouses and distribution centres.
Robotic picking systems and autonomous mobile robots significantly increase order fulfilment speed and accuracy.
Advanced sortation systems use computer vision and machine learning to process packages more efficiently. This reduces labour costs and improves throughput.
Generative AI has the potential to revolutionise supply chain management and procurement.
AI-powered systems can analyse complex variables to optimise sourcing decisions and inventory management.
Blockchain technology is enhancing supply chain transparency and traceability. This improves product authenticity verification and facilitates faster, more secure partner transactions.
Strategies for Enhancing Productivity and Operational Efficiency
Targeted improvements can significantly boost the performance of warehouses and facilities. Key areas for optimisation include inventory management, data-driven insights, and proactive maintenance approaches.
Optimising Inventory Management
Effective inventory management is crucial for warehouse productivity. Implementing lean warehousing practices can streamline operations and reduce waste.
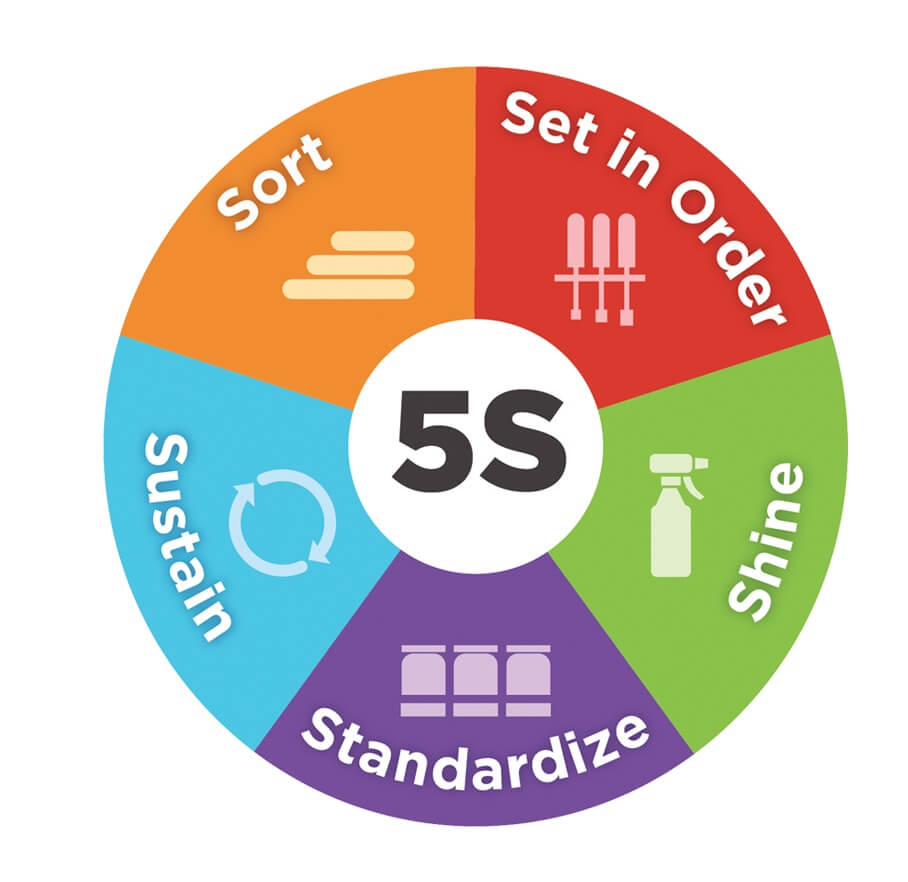
This includes adopting the “S’ methodology: Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardise, and Sustain.
Advanced inventory tracking systems use RFID and barcode technologies to provide real-time stock levels.
This accuracy helps prevent stockouts and overstocking, improving cash flow and the use of space.
Automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) can significantly enhance picking efficiency.
These systems reduce human error and increase throughput, especially in high-volume environments.
Cross-docking strategies can minimise handling and storage time for certain goods.
This approach is particularly effective for perishable items or pre-sorted shipments, reducing labour costs and improving product flow.
Leveraging Data Analytics for Operational Insights
Data analytics plays a pivotal role in modern warehouse management. Advanced analytics tools can calculate key performance indicators such as order processing times, picking accuracy, and labour efficiency.
Predictive analytics help forecast demand patterns, enabling proactive inventory management.
This foresight allows warehouses to optimise stock levels and labour allocation ahead of peak periods.
Heat mapping and spaghetti diagrams visualise warehouse traffic patterns.
These insights inform optimal product placement and picking routes, reducing travel time and enhancing productivity.
Machine learning algorithms can identify bottlenecks in processes.
By analysing vast amounts of operational data, these systems suggest targeted improvements to workflow efficiency.
Adoption of Predictive Maintenance in Facilities
Predictive maintenance strategies prevent unexpected equipment failures and costly downtime. IoT sensors on machinery collect real-time data on performance and wear.
AI-powered systems analyse this data to predict potential failures before they occur.
This proactive approach allows for scheduled maintenance during off-peak hours, minimising disruptions to operations.
Condition-based monitoring ensures that maintenance is performed only when necessary.
This optimises resource allocation and extends equipment lifespan, reducing overall maintenance costs.
Digital twins of warehouse facilities enable virtual simulations of different scenarios.
These models help test and refine maintenance strategies without risking real-world disruptions.
Cybersecurity Challenges in the Warehousing Industry
The digitalisation of warehouses brings significant cybersecurity risks. As facilities adopt advanced technologies, protecting data and systems from cyber threats becomes crucial for maintaining operational integrity and safeguarding sensitive information.
Securing the Digital Warehouse Environment
Modern warehouses rely heavily on interconnected digital systems. Robust security measures are essential to protect against unauthorised access and data breaches.
This includes implementing strong access controls, encrypting sensitive data, and regularly updating software and firmware.
Warehouses must also secure their Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
These connected sensors and equipment can be vulnerable entry points for cyber attackers. Proper network segmentation and device authentication protocols help mitigate these risks.
Employee training is critical.
Staff should be educated on cybersecurity best practices, such as recognising phishing attempts and maintaining strong passwords.
Regular security audits and penetration testing can identify vulnerabilities before they are exploited.
Protecting Inventory Tracking and Management Systems
Warehouse management systems (WMS) are prime targets for cybercriminals. These systems contain valuable data on inventory, shipments, and customer information. Ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of this data is paramount.
Multi-factor authentication should be implemented for all WMS access.
This adds an extra layer of security beyond simple passwords. Regular backups of inventory data are essential to enable quick recovery in case of a ransomware attack or system failure.
Supply chain cybersecurity is another crucial aspect.
Warehouses must vet the security practices of their partners and suppliers.
Implementing secure data exchange protocols and monitoring third-party system access can help prevent supply chain-based attacks.
Prioritising Worker Safety with Technological Solutions
Worker safety is evolving rapidly with cutting-edge technologies. Advanced solutions are transforming warehouse environments, making them safer and more efficient for employees.
Role of Technology in Ensuring Worker Safety
Wearable technologies are revolutionising worker safety. Smart helmets and vests monitor vital signs and environmental conditions, alerting supervisors to potential hazards.
IoT sensors detect dangerous gas levels and temperature fluctuations, preventing accidents before they occur.
Artificial intelligence analyses workplace data to identify risk patterns.
This predictive approach allows managers to implement targeted safety measures.
Virtual reality training programmes simulate hazardous scenarios, preparing workers for real-life emergencies without exposure to danger.
Drones conduct aerial inspections of high-risk areas, reducing the need for workers to access dangerous locations. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) handle heavy lifting tasks, minimising the risk of musculoskeletal injuries.
Collaborative Robots and Human-Robot Interaction
Collaborative robots, or cobots, are reshaping warehouse operations. These machines work alongside humans, taking on repetitive or physically demanding tasks.
Cobots are equipped with advanced sensors and safety features, allowing them to operate in close proximity to workers without risk.
Human-robot interaction is carefully designed to enhance safety.
Cobots automatically slow down or stop when humans enter their workspace. This adaptive behaviour ensures a safe working environment whilst maintaining productivity.
Cobots assist with precision tasks, reducing human error and associated risks.
They can handle hazardous materials, protecting workers from exposure to harmful substances.
As cobot technology advances, their role in ensuring worker safety will continue to expand.
Future Directions: Customisation and Competitive Advantage
Warehouses are evolving to meet specific business needs while staying ahead of competitors. Tailored processes and innovative technologies are becoming essential for success in the industry.
Customisation in Warehouse Processes for Flexibility
Warehouses are becoming more dynamic environments, adapting to unique business requirements. Companies are implementing flexible layouts and modular storage systems to accommodate changing product ranges and seasonal demands.
Customised automation solutions, such as robots programmed for specific tasks, are being deployed to enhance efficiency.
These bespoke systems allow warehouses to optimise their operations based on individual product characteristics and handling needs.
Data-driven customisation is rising, with warehouses using advanced analytics to tailor inventory management and picking strategies.
This approach enables businesses to reduce costs and improve order fulfilment accuracy.
Gaining a Competitive Edge through Innovation
Innovation is crucial for warehouses seeking to stand out in a crowded market. Digitalisation and modern operating systems are becoming standard, with companies investing in cutting-edge warehouse management software.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are leveraged to predict demand patterns and optimise stock levels.
These technologies help warehouses reduce carrying costs and improve responsiveness to market changes.
Sustainability initiatives are providing a competitive advantage.
Warehouses are adopting green technologies like solar panels and energy-efficient lighting to reduce operational costs and appeal to environmentally conscious clients.
Space optimisation innovations are crucial as warehouse costs continue to rise. Vertical storage solutions and automated storage and retrieval systems are helping businesses maximise their available space and improve efficiency.
Case Studies: Implementing Revolutionary Trends in Warehousing
Several companies have successfully adopted cutting-edge technologies to transform their warehousing operations. These implementations have yielded significant improvements in efficiency, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness.
Industry Leaders in Warehouse Digitalisation
Warehouse digitalisation has become a cornerstone of modern logistics.
Ocado, the British online supermarket, is a pioneer in this field. Its highly automated warehouses use a network of robots and conveyor systems to pick and pack groceries.
These robots communicate via 4G technology, navigating a grid system to retrieve items. This digitalisation has led to a 99% order accuracy rate and the ability to process over 65,000 orders weekly.
Another example is Amazon’s fulfilment centres. These centres streamline operations by combining robotics, machine learning, and computer vision.
Their Kiva robots have reduced order processing times from hours to minutes.
Success Stories of AI Integration in Warehousing
Artificial intelligence has revolutionised warehouse management systems.
DHL, a global logistics company, has implemented AI-powered robots in its warehouses. These robots use machine learning algorithms to optimise picking routes and improve inventory management.
The results have been remarkable, with a 25% increase in productivity and significantly reduced errors. DHL’s AI system also predicts daily order volumes, allowing for better resource allocation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What innovations are driving the future of warehouse management systems?
Advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms are revolutionising warehouse management systems. These innovations enable predictive maintenance, optimise inventory allocation, and enhance order fulfilment accuracy. Internet of Things (IoT) devices are increasingly integrated into warehouse systems. They provide real-time data on inventory levels, equipment status, and environmental conditions.
How are automation and robotics expected to transform warehouse operations by 2025?
Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) are becoming commonplace in warehouses. They efficiently navigate facilities, transport goods, and work alongside human employees to boost productivity. Robotic picking systems are improving in accuracy and speed. These systems can handle various products and package types, reducing manual labour requirements.
In what ways is the design of modern warehouses evolving to support efficient logistics?
Vertical storage solutions are gaining popularity to maximise limited warehouse space. Multi-level racking systems and mezzanines allow increased storage capacity without expanding the building footprint. Flexible layout designs accommodate changing inventory needs and technological advancements. Modular shelving and easily reconfigurable workstations support adaptable operations.
What role will artificial intelligence play in the future development of smart warehouses?
AI-powered demand forecasting systems will enhance inventory management. These systems analyse historical data, market trends, and external factors to predict future stock requirements accurately. Computer vision technology will improve quality control processes. AI algorithms can quickly inspect products for defects, ensuring only high-quality items are shipped to customers.
How is sustainable design being integrated into the warehouse and facilities industry?
Energy-efficient lighting and HVAC systems are becoming standard in modern warehouses. LED lighting with motion sensors and smart climate control systems significantly reduce energy consumption. Sustainable building materials and renewable energy sources are increasingly incorporated into warehouse construction. Solar panels, recycled materials, and green roofs contribute to reduced environmental impact.